Meta says that its shift to a Group Notes mannequin is working, primarily based on its newest Group Requirements Enforcement Report replace, which offers perception into its efforts to average content material, and tackle dangerous components throughout its apps.
As you little question recall, again in January, Meta introduced that it could be shifting to a Group Notes mannequin, following the lead of X, whereas additionally ending its third-party fact-checking course of. The thought behind this, in keeping with Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg, was that Meta had reached a degree the place it was censoring an excessive amount of, so it needed to present customers extra enter into content material choices, versus making heavy-handed choices from on excessive.
The truth that this strategy aligns with what U.S. President Donald Trump would like was utterly coincidental and had nothing to do with Meta’s strategy on this entrance.
So how is Meta measuring the success of its Group Notes initiative within the U.S.?
As per Meta:
“Of the a whole lot of billions of items of content material produced on Fb and Instagram in Q3 globally, lower than 1% was eliminated for violating our insurance policies and fewer than 0.1% was eliminated incorrectly. For the content material that was eliminated, we measured our enforcement precision – that’s, the proportion of appropriate removals out of all removals – to be greater than 90% on Fb and greater than 87% on Instagram.”
So Meta says that it’s making fewer errors, and subsequently fewer individuals are complaining about Meta’s automated system eradicating their posts incorrectly.
Which Meta says is a win, however on the identical time, in the event you’re eradicating far much less content material total, in fact there’s going to be fewer errors.
Which can be mirrored within the information. For instance, in its reporting on “Bullying and Harassment,” the speed of proactive detection from Meta’s programs, versus studies submitted by customers, has declined considerably within the final thee quarters.
Meta’s proactive detection and motion on this entrance has dropped by 20%, that means that extra customers are seeing extra violative content material.
The identical can be mirrored in its “Hateful Conduct” chart:
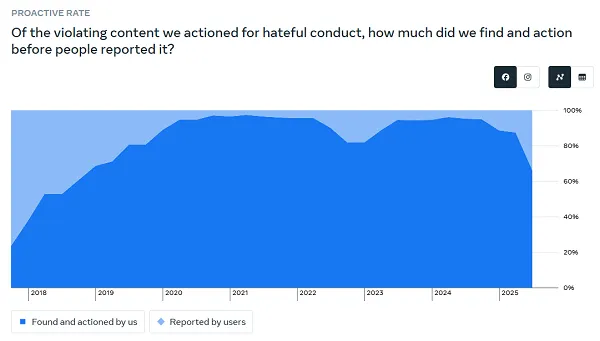
That final dip within the chart is a big decline in proactive enforcement, in what’s lengthy been a problematic space, when it comes to social media amplification.
So whereas Meta would possibly effectively be making fewer errors in over-enforcement, and penalizing customers incorrectly, which is according to the extra “freedom of speech” fashion strategy that Zuck and Co. are aiming for, the trade-off is that extra folks throughout its apps are being uncovered to extra doubtlessly dangerous content material consequently. Which, primarily based on the declining charts above, Meta’s programs may detect and take away, however as an alternative, it is opting to let extra by way of, and it is promoting this as a constructive, as a result of folks aren’t being restricted as a lot.
Basically, whereas Meta’s saying that “enforcement precision” was at 90%, it’s tough to quantify the success of Group Notes as an alternative choice to systematic enforcement, if the one measure is consumer complaints, or not.
By way of particular coverage areas, Meta says that:
“On each Fb and Instagram, prevalence elevated for grownup nudity and sexual exercise, and for violent and graphic content material, and on Fb it elevated for bullying and harassment. That is largely because of adjustments made throughout the quarter to enhance reviewer coaching and improve assessment workflows, which impacts how samples are labeled when measuring prevalence.”
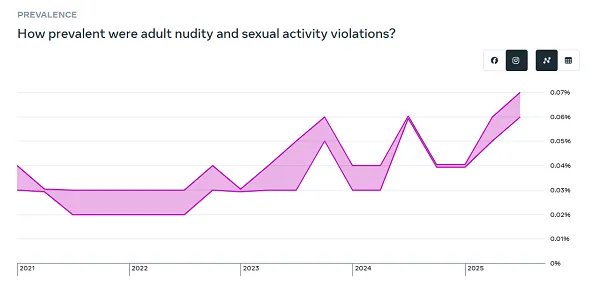
Given this proviso, it’s exhausting to say whether or not this can be a important level of notice or not, as a result of Meta’s saying that the rise is barely because of a change in methodology.
So possibly these spikes are value noting, possibly they’re really indicators of enchancment.
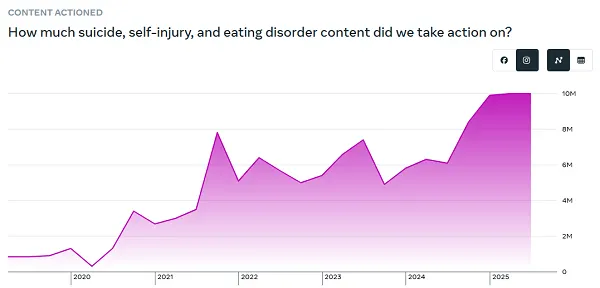
Although in mild of the latest push to extend social media restrictions amongst younger teenagers, this chart stays a priority:
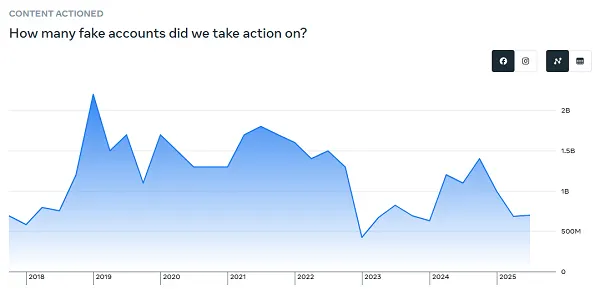
By way of faux accounts, Meta maintains that round 4% of its greater than 3 billion month-to-month energetic customers are fakes.
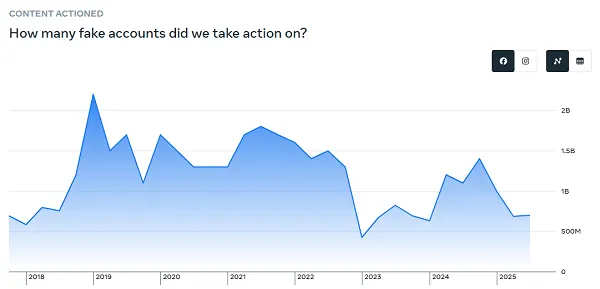
Many have questioned this, primarily based on their very own experiences of faux profiles on Fb and IG. Although today, it’s exhausting to inform what’s a faux profile, and what’s AI, and whether or not each are thought-about to be the identical factor? I imply, Meta has been engaged on a challenge so as to add in AI profiles to its apps, which is able to work together like actual folks. So are these fakes?
Both approach, for context, 4% of three.54 billion complete customers nonetheless equates to greater than 140 million faux profiles in its apps, which Meta is formally acknowledging.
So there’s that.
Meta has additionally printed an replace to its “Extensively Seen Content material Report,” which offers extra context round what individuals are really seeing on Fb within the U.S.
The report was initially launched again in 2021, with a purpose to dispel the notion that Fb’s algorithms amplify divisive content material and misinformation. By exhibiting what kinds of posts and Pages really see essentially the most engagement, Meta’s in search of to spotlight that it’s not as large of an issue on this respect as folks would possibly understand, although once more, I might notice that at Meta’s scale, even content material that will get comparatively small traction remains to be reaching doubtlessly thousands and thousands of individuals.
However when it comes to what’s getting essentially the most attain, Meta studies that it’s principally trending information tales that Fb customers are most occupied with.
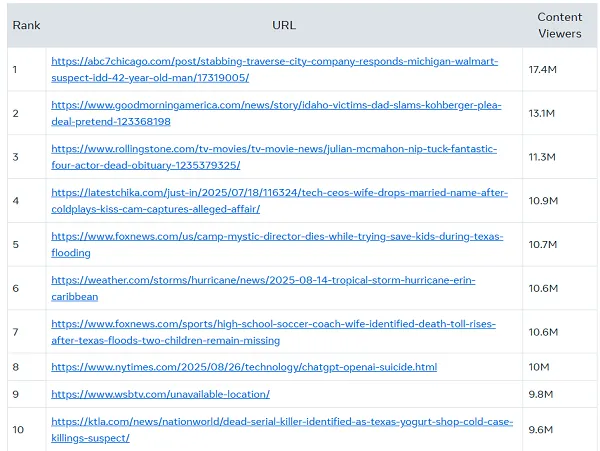
Crime tales, the loss of life of actor Julian McMahon, the Coldplay live performance couple, these are the kinds of updates that gained essentially the most traction on Fb in Q3.
So it’s not politically divisive stuff, it’s intriguing tales of real-life occasions. Which is definitely higher than the standard content material that populates this record (usually, tabloid gossip wins out), however the backside line that Fb desires to place ahead is that political content material will not be a serious component of dialogue within the app.
Although, total, it’s value noting that the share of consideration for prime posts is miniscule at Fb’s scale.
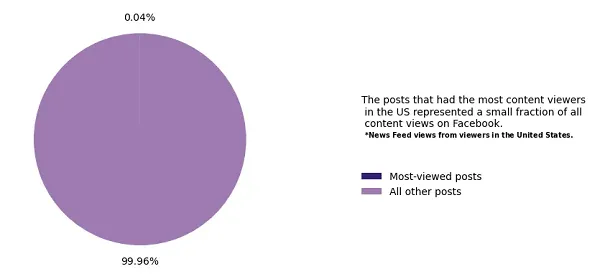
In broader context, the platform’s scale and attain is so large that any amplification is critical, so even with these notes on essentially the most shared posts, we’re not likely getting a lot of an understanding of Fb’s total affect on this respect.
Oh, there’s additionally this chart, which digital entrepreneurs hate:
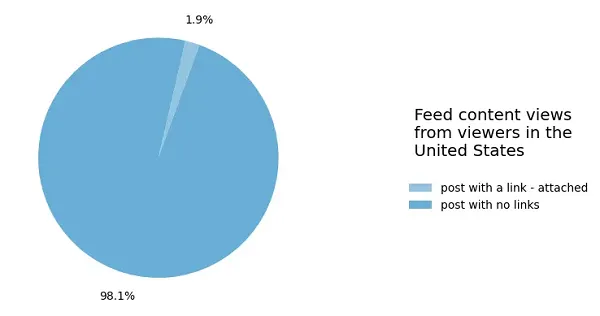
Hyperlink posts are a tiny, tiny a part of Fb total, so in the event you’re seeking to drive site visitors, you’re prone to be upset.
The prevalence of hyperlink posts has decreased from Q1, when it was at 2.7%, whereas again in 2022, it was at 9.8%.
So a big decline for hyperlink posts within the app.
General, there’s no main standout findings in Meta’s newest transparency studies, with its efforts to evolve moderation resulting in fewer errors, however doubtlessly extra publicity to hurt consequently. Although in Meta’s metrics, it’s doing higher on this entrance as effectively.